Baruteau, A-E;
Kyndt, F;
Behr, ER;
Vink, AS;
Lachaud, M;
Joong, A;
Schott, J-J;
Horie, M;
Denjoy, I;
Crotti, L;
et al.
Baruteau, A-E; Kyndt, F; Behr, ER; Vink, AS; Lachaud, M; Joong, A; Schott, J-J; Horie, M; Denjoy, I; Crotti, L; Shimizu, W; Bos, JM; Stephenson, EA; Wong, L; Abrams, DJ; Davis, AM; Winbo, A; Dubin, AM; Sanatani, S; Liberman, L; Kaski, JP; Rudic, B; Kwok, SY; Rieubland, C; Tfelt-Hansen, J; Van Hare, GF; Guyomarc'h-Delasalle, B; Blom, NA; Wijeyeratne, YD; Gourraud, J-B; Le Marec, H; Ozawa, J; Fressart, V; Lupoglazoff, J-M; Dagradi, F; Spazzolini, C; Aiba, T; Tester, DJ; Zahavich, LA; Beauséjour-Ladouceur, V; Jadhav, M; Skinner, JR; Franciosi, S; Krahn, AD; Abdelsayed, M; Ruben, PC; Yung, T-C; Ackerman, MJ; Wilde, AA; Schwartz, PJ; Probst, V
(2018)
SCN5A mutations in 442 neonates and children: genotype-phenotype correlation and identification of higher-risk subgroups.
Eur Heart J, 39 (31).
pp. 2879-2887.
ISSN 1522-9645
https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy412
SGUL Authors: Behr, Elijah Raphael
|
Microsoft Word (.docx)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (211kB) |
||
|
Image (TIFF) (Figure 1)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
|
Image (TIFF) (Figure 2)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
|
Image (TIFF) (Figure 3)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (918kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](http://sgultest.da.ulcc.ac.uk/110038/24.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Baruteau-R1-Figure%204.gif)
|
Image (GIF) (Figure 4)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (35kB) | Preview |
|
|
Microsoft Word (.docx) (Supplemental materials)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (772kB) |
Abstract
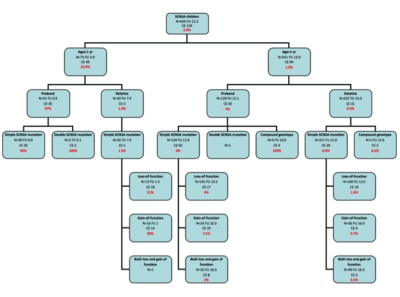
Aims: To clarify the clinical characteristics and outcomes of children with SCN5A-mediated disease and to improve their risk stratification. Methods and results: A multicentre, international, retrospective cohort study was conducted in 25 tertiary hospitals in 13 countries between 1990 and 2015. All patients ≤16 years of age diagnosed with a genetically confirmed SCN5A mutation were included in the analysis. There was no restriction made based on their clinical diagnosis. A total of 442 children {55.7% boys, 40.3% probands, median age: 8.0 [interquartile range (IQR) 9.5] years} from 350 families were included; 67.9% were asymptomatic at diagnosis. Four main phenotypes were identified: isolated progressive cardiac conduction disorders (25.6%), overlap phenotype (15.6%), isolated long QT syndrome type 3 (10.6%), and isolated Brugada syndrome type 1 (1.8%); 44.3% had a negative electrocardiogram phenotype. During a median follow-up of 5.9 (IQR 5.9) years, 272 cardiac events (CEs) occurred in 139 (31.5%) patients. Patients whose mutation localized in the C-terminus had a lower risk. Compound genotype, both gain- and loss-of-function SCN5A mutation, age ≤1 year at diagnosis in probands and age ≤1 year at diagnosis in non-probands were independent predictors of CE. Conclusion: In this large paediatric cohort of SCN5A mutation-positive subjects, cardiac conduction disorders were the most prevalent phenotype; CEs occurred in about one-third of genotype-positive children, and several independent risk factors were identified, including age ≤1 year at diagnosis, compound mutation, and mutation with both gain- and loss-of-function.
| Item Type: | Article | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additional Information: | This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced version of an article accepted for publication in European Heart Journal following peer review. The version of record Alban-Elouen Baruteau, Florence Kyndt, Elijah R Behr, Arja S Vink, Matthias Lachaud, Anna Joong, Jean-Jacques Schott, Minoru Horie, Isabelle Denjoy, Lia Crotti, Wataru Shimizu, Johan M Bos, Elizabeth A Stephenson, Leonie Wong, Dominic J Abrams, Andrew M Davis, Annika Winbo, Anne M Dubin, Shubhayan Sanatani, Leonardo Liberman, Juan Pablo Kaski, Boris Rudic, Sit Yee Kwok, Claudine Rieubland, Jacob Tfelt-Hansen, George F Van Hare, Béatrice Guyomarc’h-Delasalle, Nico A Blom, Yanushi D Wijeyeratne, Jean-Baptiste Gourraud, Hervé Le Marec, Junichi Ozawa, Véronique Fressart, Jean-Marc Lupoglazoff, Federica Dagradi, Carla Spazzolini, Takeshi Aiba, David J Tester, Laura A Zahavich, Virginie Beauséjour-Ladouceur, Mangesh Jadhav, Jonathan R Skinner, Sonia Franciosi, Andrew D Krahn, Mena Abdelsayed, Peter C Ruben, Tak-Cheung Yung, Michael J Ackerman, Arthur A Wilde, Peter J Schwartz, Vincent Probst; SCN5A mutations in 442 neonates and children: genotype–phenotype correlation and identification of higher-risk subgroups, European Heart Journal, Volume 39, Issue 31, 14 August 2018, Pages 2879–2887, is available online at: https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy412 | ||||||||
| Keywords: | Cardiovascular System & Hematology, 1102 Cardiovascular Medicine And Haematology | ||||||||
| SGUL Research Institute / Research Centre: | Academic Structure > Molecular and Clinical Sciences Research Institute (MCS) | ||||||||
| Journal or Publication Title: | Eur Heart J | ||||||||
| ISSN: | 1522-9645 | ||||||||
| Language: | eng | ||||||||
| Dates: |
|
||||||||
| Publisher License: | Publisher's own licence | ||||||||
| PubMed ID: | 30059973 | ||||||||
 |
Go to PubMed abstract | ||||||||
| URI: | http://sgultest.da.ulcc.ac.uk/id/eprint/110038 | ||||||||
| Publisher's version: | https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy412 |
Statistics
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |